Trading Accounts
Trading Conditions
Financials
CFD Trading instruments

Don’t waste your time – keep track of how NFP affects the US dollar!
The ASIC policy prohibits us from providing services to clients in your region. Are you already registered with FBS and want to continue working in your Personal area?
Personal areaInformation is not investment advice
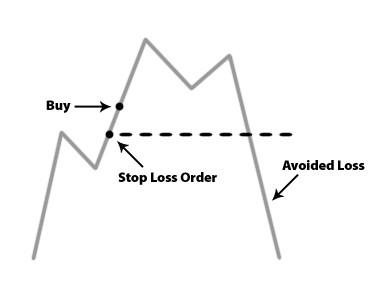
A Stop Loss is an exit order, which is used to limit the amount of loss that a trader may take on a trade if the trade goes against him. In addition, it eliminates the anxiety every trader inevitable faces with being in a losing trade without a plan. No trading system will bring profit on every trade, and losses are natural. Successful risk management means that the losses should be minimized. Stop loss order can be an efficient solution for that.
If you’ve decided to use a stop loss order, it’s very important to find a good place for it. If the stop order is too close to the current price, there’s a risk that the volatile price will hit this order during a false move and then go in the direction you’ve expected it to, so you’ll lose money and earn nothing. If the Stop order is too far from the current price, a trader may be vulnerable to a big loss in case the market reverses contrary to his expectations.

There are many types of Stop Loss orders. Here’s an algorithm for choosing the one that fits you.
The position of a Stop Loss may depend on whether you are a discretionary or a system trader. In discretionary trading, it’s the trader himself/herself who every time decides which trades to make. A trader places Stop order at a price at which he/she doesn’t expect the market to trade. By doing so, he/she may take into consideration different factors, which may differ from trade to trade.
In system trading, trading decisions are made by a trading system. A trader either opens positions manually in line with the trade system’s signals or trading is automated. Here Stop Loss orders are placed according to risk/reward and win/loss ratios of the trading system.
The size of such Stop is derived from the size of the trader’s account. The most common one is 1% of an account on one trade. For example, if your equity is $1000, you can afford losing $10 on, let’s say, buying EUR/USD. That’s 100 pips on a 0.01 lot (1 micro lot). The upper limit for such a Stop is considered to be at 5%. As you may see, such approach doesn’t constitute a logical response to what’s actually happening at the price chart.
The size of this stop depends on the technical analysis of the price action conducted by a trader. Here one usually identifies support level and puts Stop Loss order for a long position below it. Technically oriented traders like to combine these exit points with equity Stop rules to formulate charts stops. Such Stops are often placed at swing highs/lows.
The size of this stop depends on the size of volatility at the market. If the volatility is high and price makes big swings, a trader needs bigger Stop in order to avoid getting stopped out. In case of lower volatility, a trader places smaller Stops. Volatility can be measured with help of such indicators as Bollinger Bands.
Time Stops are based on a predetermined time of a trade. Imagine you are a day trader, you trade only in specific session and close your positions before it ends. You can set a time limit, at which you position will be closed. You can do this with the help of Expert Advisors (EA) or, in other words, trading robots.
There’s also one aggressive approach to Forex trading, which we don’t recommend all that much. Some traders use the fact that Forex dealers can liquidate their customer positions almost as soon as they trigger a margin call level. A trader may divide capital into several equal parts and put only one at the account. Then he/she chooses position size and potential margin call acts as a Stop Loss. We warn you that it’s sensible to make such trades only with small amounts of money. Note that it will prevent you from having more than one open position at a time.
Static Stop retains its place once it’s set. Trailing Stop is adjusted as the trade moves in the trader’s favor in order to further reduce the risk of being incorrect in a trade.
For example, a trader opened a long position on EUR/USD at $1.3100, with a 50 pip Stop at $1.3050 and a 150 pip Take Profit at $1.3200. No changes will be made to your order until the profit on your open position exceeds 50 pips. If euro rises by 50 pips to $1.3150, the trader may adjust his stop up by 50 pips to $1.3100. When you move your Stop Loss to the market entry level (like it happens in this case), it becomes a break-even Stop: if the price reverses and a trader’s Stop is hit, he/she won’t gain any money but will lose none either. Each time the price moves 50 pips from the current Stop Loss in a trader’s favor, an order will be sent out by the server to change the level of the current Stop Loss to be within 50 pips of the current price. In other words, Trailing Stop automatically moves your Stop Loss order following the price. If the price then turns against the trader, the Stop Loss isn’t moved anymore.
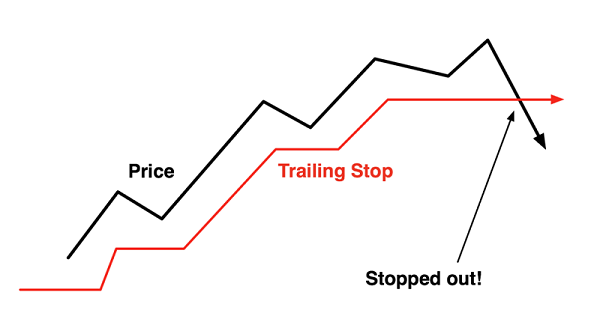
Trailing Stops are mainly used by traders who like trading trends, but haven’t got a possibility to track the price action all the time.
Once Stop Loss is set, don’t widen it. Move your stops only in the direction of the trade (Trailing Stops). You have already made your decision. If the market went against you and your Stop was hit, analyze your trade and see what you’ve done wrong. You don’t need to become overly upset about the failure. What you need is to be successful in your next trade, so move on to the next opportunity.